Alligator Creek (2030) (Tidal Segment), covering 172 acres, is a bay situated in Sarasota County, with the associated WBID(s): 2030.
Note that this waterbody is impaired for one or more parameters including Mercury. All recreational marine waters in Florida are impaired for Mercury based on fish tissue assessments and a statewide Total Maximum Daily Load (TMDL) pollutant limit for Mercury has been adopted in response. The largest sources of Mercury are from air pollution generated from local and global power plants.
This waterbody is located within: Lemon Bay Basin
This waterbody is impaired according to the Florida Dept. of Environmental Protection's (FDEP) implementation of the Impaired Waters Rule (IWR). The FDEP evaluates whether waters meet their designated uses, which include aquatic life use support, primary contact and recreation use support, fish and shellfish consumption use support, and drinking water use support. View the full impaired waters section »
Impairment Status
Impaired
Water Body Class(es)
3M
Water Body Type(s)
ESTUARY
View Maps / Data
CHNEP's Comprehensive Conservation and Management Plan (CCMP) identified four action plans: water quality improvement; hydrological restoration; fish, wildlife, and habitat improvement; and public engagement. Click on the interactive maps below to view data associated with these goals and actions.
Water Quality Snapshot
The Water Quality Snapshot compares the most current water quality data to applicable water quality standards for Chlorophyll a, Phosphorus, Nitrogen, Bacteria, and Dissolved Oxygen to provide a snapshot of how a waterbody is doing. Water quality standards are outlined in Florida Administrative Code 62-302 for fresh/marine waterbodies of different types and uses. A Water Body Identification number (WBID) is an assessment unit that is intended to represent Florida’s waterbodies at the watershed or sub-watershed scale. The assessment units are drainage basins, lakes, lake drainage areas, springs, rivers and streams, segments of rivers and streams, coastal, bay and estuarine waters in Florida.
There are no WBIDs with water quality data at this time.
View Detailed Data About the Following Topics:
Water Quality(Red Tide, Nutrient Chemistry, Water Clarity, Salinity, Bacteria, Dissolved Oxygen, Other Indicators, Impaired Waters)
Red Tide
The Gulf and bays of southwest Florida experience a "red tide" that is caused by recurring high concentrations of an alga that discolors the water and releases toxic chemicals. In Florida, under suitable conditions, the microscopic organism Karenia brevis successfully reproduces to more than a million cells per liter. The toxins kill fish, manatees, birds, and other wildlife, make shellfish inedible, and make beachgoers uncomfortable. The economic losses to the recreation industry can exceed tens of millions of dollars. Public outcry about persistent red tides has stimulated an increased resolve among researchers to understand the complex bloom mechanisms and to develop methods to alleviate the troublesome effects.
Learn more about Red Tide »
No Data Available
Nutrient Chemistry
Although naturally present in all surface waters, excessive nutrients – nitrogen and phosphorus – are a nationwide water quality problem. They can cause overgrowth of plants that deplete the oxygen in the water needed by aquatic creatures to survive. Learn more about nutrient chemistry »
| Parameter | Latest Value | Historic Range | Graphs (click to enlarge) and Data | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen, Total | 1.32 mg/L 12/23/2024 Source: Sarasota County Coastal Creeks | 0.72 - 5.43 mg/L 3/25/2013 - 12/23/2024 138 samples |  | Download Data |
| Phosphorus as P | 0.5 mg/L 12/23/2024 Source: Sarasota County Coastal Creeks | 0.24 - 1.55 mg/L 11/14/2013 - 12/23/2024 96 samples |  | Download Data |
| Chlorophyll a, uncorrected for pheophytin | 47 µg/L 7/7/2020 Source: FDEP - South Regional Operations Center | 9.8 - 120 µg/L 3/8/2018 - 7/7/2020 7 samples | 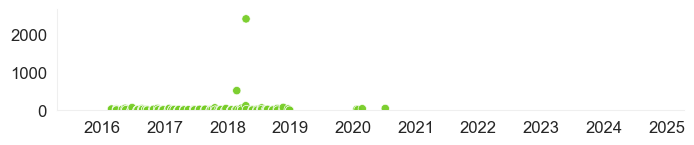 | Download Data |
| Chlorophyll a, corrected for pheophytin | 5.08 µg/L 12/23/2024 Source: Sarasota County Coastal Creeks | 0.38 - 43.7 µg/L 3/25/2013 - 12/23/2024 155 samples |  | Download Data |
| Nitrogen, ammonia as N | 0.01 mg/L 12/23/2024 Source: Sarasota County Coastal Creeks | 0 - 0.25 mg/L 3/25/2013 - 12/23/2024 118 samples |  | Download Data |
| Nitrogen, Kjeldahl | 1.15 mg/L 12/23/2024 Source: Sarasota County Coastal Creeks | 0.32 - 3.44 mg/L 3/25/2013 - 12/23/2024 96 samples |  | Download Data |
| Nitrogen, Nitrite + Nitrate as N | 0.17 mg/L 12/23/2024 Source: Sarasota County Coastal Creeks | 0.02 - 1.19 mg/L 3/25/2013 - 12/23/2024 100 samples |  | Download Data |
Water Clarity
Water clarity or turbidity measurements show the degree to which light is blocked by suspended particles such as sediment or algae. In a healthy aquatic system, sunlight is able to penetrate the water column and is available for photosynthetic plants and the creatures that depend on them. Learn more about water clarity »
| Parameter | Latest Value | Historic Range | Graphs (click to enlarge) and Data | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Secchi disk depth | 0.98 ft. 10/28/2024 Source: FDEP - South Regional Operations Center | 0.98 - 4.27 ft. 3/8/2018 - 10/28/2024 12 samples |  | Download Data |
| Turbidity | 6.1 NTU 5/21/2024 Source: Sarasota County Coastal Creeks | 0.93 - 13 NTU 7/28/2006 - 5/21/2024 158 samples |  | Download Data |
| Apparent Color | 90 PCU 12/17/2020 Source: Sarasota County Coastal Creeks | 75 - 180 PCU 3/25/2013 - 12/17/2020 106 samples |  | Download Data |
Salinity
Salinity is a measure of the amount of salts dissolved in water. An estuary can exhibit a change in salinity throughout its length as fresh water entering from the tributaries mixes with seawater from the ocean. Learn more about salinity »
| Parameter | Latest Value | Historic Range | Graphs (click to enlarge) and Data | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salinity | 5.12 ppt 10/28/2024 Source: FDEP - South Regional Operations Center | 0.36 - 19.25 ppt 7/16/2018 - 10/28/2024 10 samples |  | Download Data |
| Specific conductance | 9,011 umho 10/28/2024 Source: FDEP - South Regional Operations Center | 749 - 30,952 umho 3/8/2018 - 10/28/2024 13 samples |  | Download Data |
Bacteria
Bacterial indicators for recreational waters include Fecal Coliform, Total Coliform, and Enterococcus (including E. coli). While indicator organisms themselves are not necessarily pathogenic, their presence suggests possible contamination which may result in human illness. Sources of this contamination include stormwater runoff, sewage overflows, and feces from wild and domestic animals. Learn more about bacteria »
| Parameter | Latest Value | Historic Range | Graphs (click to enlarge) and Data | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fecal Coliform | 440 cfu/100mL 12/17/2024 Source: Sarasota County Coastal Creeks | 10 - 132,000 cfu/100mL 7/28/2006 - 12/17/2024 257 samples |  | Download Data |
| Enterococcus Group Bacteria | 743 cfu/100mL 12/17/2024 Source: Sarasota County Coastal Creeks | 10 - 18,000 cfu/100mL 4/23/2015 - 12/17/2024 153 samples |  | Download Data |
| Escherichia coli | 554 cfu/100mL 12/23/2024 Source: Sarasota County Coastal Creeks | 61 - 17,329 cfu/100mL 10/19/2017 - 12/23/2024 97 samples |  | Download Data |
Dissolved Oxygen
Dissolved Oxygen (DO) is one of the most important indicators of water quality. It is essential for a healthy, productive biological system and vital to the survival of fish and other aquatic organisms. Learn more about dissolved oxygen »
| Parameter | Latest Value | Historic Range | Graphs (click to enlarge) and Data | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dissolved Oxygen (DO) | 2.18 mg/L 10/28/2024 Source: FDEP - South Regional Operations Center | 0.61 - 6.5 mg/L 3/8/2018 - 10/28/2024 13 samples |  | Download Data |
| BOD, Biochemical oxygen demand | 5.85 mg/L 12/23/2024 Source: Sarasota County Coastal Creeks | 0.5 - 8.47 mg/L 3/25/2013 - 12/23/2024 125 samples |  | Download Data |
| Dissolved oxygen saturation | 28 percent (%) 10/28/2024 Source: FDEP - South Regional Operations Center | 9.3 - 80 percent (%) 3/8/2018 - 10/28/2024 13 samples |  | Download Data |
Other Indicators
| Parameter | Latest Value | Historic Range | Graphs (click to enlarge) and Data | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 7.32 10/28/2024 Source: FDEP - South Regional Operations Center | 6.99 - 7.84 3/8/2018 - 10/28/2024 13 samples | 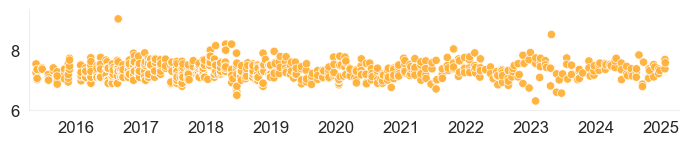 | Download Data |
| Temperature, water | 76.82 °F 10/28/2024 Source: FDEP - South Regional Operations Center | 62.96 - 88.88 °F 3/8/2018 - 10/28/2024 13 samples |  | Download Data |
Impaired Waters
This waterbody is impaired according to the Florida Dept. of Environmental Protection's (FDEP) implementation of the Impaired Waters Rule (IWR). The FDEP evaluates whether waters meet their designated uses, which include aquatic life use support, primary contact and recreation use support, fish and shellfish consumption use support, and drinking water use support. Learn more about IWR Assessment »
Impairment Status
Impaired
Water Body Class(es)
3M
Water Body Type(s)
ESTUARY
Florida also has mercury impairment statewide, its largest source being atmospheric deposition from local and global power generation. The Florida Department of Health (DOH) and Florida Department of Environmental Protection have identified over 400 waterbodies, most freshwater lakes and rivers but also some coastal/marine areas, that are impaired due to mercury found in fish tissue. Florida Fish Consumption Advisories, updated annually by the DOH, provide guidance on how to limit mercury exposure from these waters.
This waterbody is associated with the following DEP Waterbody IDs (WBIDs) and impairment statuses:
| WBID | Name | Impairment(s) | Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2030 | Alligator Creek (Tidal Segment) | Dissolved Oxygen (Percent Saturation) | Ongoing Restoration Activities |
| 2030 | Alligator Creek (Tidal Segment) | Enterococci | Impaired |
| 2030 | Alligator Creek (Tidal Segment) | Mercury (in fish tissue) | TMDL Complete |
| 2030 | Alligator Creek (Tidal Segment) | Nutrients (Chlorophyll-a) | Ongoing Restoration Activities |
Source: Florida Department of Environmental Protection
Related Documents and Links
- Alligator Creek FDEP 319(h) Water Quality Monitoring Program Quality Assurance Project Plan
- Alligator Creek WBID 2030 TMDL Implementation Plan
- Final Report: Mercury TMDL for the State of Florida
- Letter: TMDL for Nutrients, Dissolved Oxygen & Coliforms in Sarasota/Charlotte Harbor Basin Groups
- Memo: Approval of Proposed Schedule for TMDL Elements of NPDES/MS4 Permit
- Numeric Nutrient Criteria Compliance for Sarasota County, Florida, 2007-2011
- Proposed Numeric Nutrient Criteria for the CHNEP Estuarine System (Draft)
- Responsiveness Summary TMDL Development for Sarasota Bay / Charlotte Harbor.....
- TMDL for Nutrients, Dissolved Oxygen, and Coliforms in Sarasota Bay/Charlotte Harbor (10 WBIDs)
- Withdrawal Letter for Alligator Creek DO TMDL
Habitats / Ecology(Seagrass Coverage, Artificial Reefs)
Seagrass Coverage
Among the most important habitats in Florida's estuarine environments, seagrass beds are indispensable for the role they play in cycling nutrients, supplying food for wildlife, stabilizing sediments, and providing habitat for juvenile and adult finfish and shellfish. Use the interactive map below to observe the size, density and location of seagrass beds from year to year. The graph shows how the total amount of seagrass in the bay has changed over time. Learn more about seagrasses »
The interactive map below shows seagrass extents as they existed between 1948 and 2022. Use the slider to toggle the year being displayed to demonstrate how seagrass coverage has changed over time. Note: Seagrass acreage data are collected bi-annually by each Water Management District in alternate years. As a result, some years have no acreage data.
2022 Seagrass Coverage
Artificial Reefs
Artificial reefs are created by the placing building materials, derelict vessels, or other objects in carefully selected nearshor or offshore locations. Once the reef structure is established, tiny free-floating creatures soon attach and grow, quickly attracting larger marine life. These lush, natural-looking reefs replace lost habitats and also create recreational opportunities for anglers and divers. Learn more about artificial reefs »
Find Artificial Reefs
No Data Available
Recreation
Find maps and waterway navigation guides, descriptions of facilities and recreational amenities, as well as warnings and restrictions pertaining to their use.
Photos
Click on a thumbnail photograph to view the full size version with credits and a description.

Trim the Grass
Credit: John Ryan, Sarasota County Public Utilities
_Hydrograss and Plantings_12-9-2013.JPG)
Hydroseeded creek banks
Credit: Sarasota County Government

Aerial view of ICW and US Hwy 41
Credit: Amanda Dominguez, Sarasota County Government

South Venice foot bridge
Credit: Lionel Murphy Jr. Venice Area Chamber of Commerce.

Aerial view of Intracoastal Waterway Venice
Credit: Evan Brown

Hydroseed Spraying Banks
Credit: John Ryan, Sarasota County Public Utilities

Group Photo from BCC approval day
Credit: John Ryan, Sarasota County Public Utilities

Alligator Creek, looking northeast
Credit: Amanda Dominguez

Volunteers who took part in a work session on 6/21/2014
Credit: South Venice Water Quality Task Force

Map showing location of Lemon Bay
Credit: Sarasota County Environmental Services

Aerial view of Alligator Creek
Credit: John Ryan

Intracoastal Waterway in Venice from Venice Blvd.
Credit: Greg Wahl

Audubon rookery pond closeup, Annex Road, Venice.
Credit: Sarasota Bay National Estuary Program

Aerial view of Intracoastal Waterway
Credit: Amanda Dominguez

Stump Pass
Credit: Mike Herms

Aerial view of Alligator Creek Trail
Credit: John Ryan, Sarasota County

Siesta Waterway, downstream
Credit: John Ryan, Sarasota County Public Utilities

Bridge across Lemon Bay
Credit: History Center

Alligator Creek Trail
Credit: John Ryan, Sarasota County Public Utilities

Lemon Bay in Engelwood from Beach Road
Credit: Greg Wahl
Related Information
education Links
- Fishing Cultures of Southwest Florida
- Greater Charlotte Harbor Watershed Guide - An Educational Guide to Ecological Explorations...
fish and Wildlife Links
- CHEC Bird Sighting Data from Cedar Point Environmental Park
- Christmas Bird Count Data Summary for Venice, Florida, 2001-2013
- Fishes of the Lemon Bay estuary and a comparison of fish community structure to nearby estuaries...
- Lemon Bay Shellfish Harvesting Map
- Sarasota County Manatee Protection Plan (2011 Update)
- Sealife in Southwest Florida Estuaries
- Tarpon Tagging Project Brochure
- Thornton Key Preserve
- Venice Rookery Bird Checklist
general Links
- A History of the Sarasota County Gun Range Site
- Alligator Creek Sediment Management Plan Final Report
- Cooperative Funding Agreement (SWFWMD, Sarasota County): South Venice Waterway Restoration Project
- Dona Bay Watershed Management Plan (outline with links to chapters)
- Final Report on the Development of a Tidal Creek Condition Index for Sarasota County
- Florida's Endangered and Threatened Species 2013
- Lemon Bay Water Quality Data Collected by Englewood Jaycees (1991-92)
- Lemon Bay Watershed Management Plan (outline with links to chapters)
- Lemon Bay Watershed Management Plan--Summary Presentation
- Linkages between tidal creek ecosystems and the landscape and demographic attributes
habitats and Ecology Links
- 2012 Bay Scallop Summary: Lemon Bay and Gasparilla Sound
- 2021 Florida Macroalgae Workshops
- A Fresh Look at Ecological Condition Indices for Southwest Florida's Urbanizing Tidal Streams
- An Assessment of Florida Red Tide: Causes, Consequences and Management Strategies
- Appendices to Identifying Pot. Drivers of Change in Seagrass/Algal Community Composition in SWFL APs
- Bay scallop data for Lemon Bay and Gasparilla Sound, 2009-2015
- Charlotte Harbor Benthic Biodiversity Report
- Coastal Scrub Restoration: A Case Study for the Urban Interface
- Common Macrobenthic invertebrates of Charlotte Harbor
- Counts of Red Tide Organisms 1954-57
programs & Projects Links
- About the Charlotte Harbor Estuaries Volunteer Water Quality Monitoring Program (CHEVWQMN)
- Charlotte Harbor Aquatic Preserve Map
- Charlotte Harbor Aquatic Preserves Management Plan (2016)
- Charlotte Harbor Estuaries Volunteer Water Quality Monitoring Network (CHEVWQMN) Metadata
- Englewood Water District
- FYI / Lemon Bay Park Volunteers
- Lemon Bay Aquatic Preserve
- Lemon Bay Aquatic Preserve Brochure
- Lemon Bay Conservancy
- Lemon Bay League, Inc.
recreation Links
- (Charlotte County) Blueways Trails: A guide for the canoe/kayak enthusiast.
- Amberjack Environmental Park
- Ann and Chuck Dever Regional Park
- Bill Coy/Buck Creek Preserve
- Boating and Angling Guide to Charlotte Harbor (online version)
- Boating and Seagrasses (video)
- Cedar Point Environmental Park
- Charlotte County Environmental Parks & Preserves
- Fishing, Boat Ramps, Kayak Launches
- Florida Circumnavigational Saltwater Paddling Trail Segment 10: Sarasota/Venice
stormwater Links
- Alligator Creek Stormwater Treatment Project Fact Sheet
- Alligator Creek Stormwater Treatment Trains - Final Report
- Briarwood Stormwater Treatment Facility - Schematic diagram
- Rethinking altered drainage systems: giving the river what it needs
- South County Alligator Creek Stormwater Treatment System Presentation
- Stormwater Capital Improvement Program Lemon Bay Watershed
- Stormwater: A Mixed Blessing
- Technical Memorandum: Briarwood Stormwater Treatment Facility
water Levels and Flows Links
- Coastal Fringe Phase 2 Lemon Bay Watershed Management Plan Final Report
- Island of Venice Flood Study Update
- Lemon Bay Preserve Weir Project Location
- Sarasota Bay Estuary Program’s Sea Level Rise (SLR) Brochure 2014
- Tidal Flux in Northern Lemon Bay - graph of observations 1970s.
water Quality Links
- A Spectral Optical Model and a Water Clarity Reporting Tool for Seagrasses
- A spectral optical model and updated water clarity reporting tool for Charlotte Harbor seagrasses
- Alligator Creek FDEP 319(h) Water Quality Monitoring Program Final Report
- Alligator Creek FDEP 319(h) Water Quality Monitoring Program Quality Assurance Project Plan
- Alligator Creek Watershed Water Quality Summary
- Alligator Creek WBID 2030 TMDL Implementation Plan
- Approval Letter for Alligator Creek Implementation Plan
- Assessment of Present and Future Nitrogen Loads, Water Quality, and Seagrass... in Lemon Bay
- Charlotte Harbor & Estero Bay Aquatic Preserves Water Quality Status & Trends for 1998-2005
- Charlotte Harbor Numeric Nutrient Criteria: Task 11 – Implementation Issues
2 Year Graph
10 Year Graph
Seasonal Variation Graph
Graph Details and Help
Water quality data is displayed as a scatter-plot with data from individual sampling events displayed by date, for the previous two- and ten-year periods. Data from all available sources are plotted together. Clicking on a graph will open a larger version of it. To view/download data older than ten years, or to view/download data from individual data source(s), click the "Download Data" icon or button.
The scale used is chosen to accommodate typical values for the water quality parameter being graphed. Units are shown on the y-axis and in the graph title.
Graphs are generated and stored in the Water Atlas database on a periodic basis using an automated process. The date when the graph was created is shown.
The Seasonal Variation Graph displays a statistical summary of data from all available data sources for the entire period of record. It is used to illustrate typical variation in the selected water quality parameter from month to month during the year. The diagram below shows how to read the graph:

The median value is shown. Although not specifically marked on the graph, the mean (average) value is midway between the 25th and 75th percentiles.
The "whiskers" indicate the range of the sample values; those that are outside pre-defined "Minimum" and "Maximum" values are excluded. Sample data less than the Minimum or greater than the Maximum are considered to be outliers and are not displayed on the graph.







